
Since 2018, the US-China trade relationship has been on rocky ground due to increased tariffs imposed under Section 301 policies.
USA Customs Clearance has successfully worked with hundreds of importers sourcing their products from China. Let’s review what Section 301 tariffs are, and get clued in on which goods it applies to and which it doesn’t.
For the purposes of international trade, Section 301 tariffs refer to any additional tax and duty being applied to imports coming from nations that the US feels are violating fair trade practices.
The Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) is the agency that conducts the investigations on countries that are suspected of trade agreement violations and takes the necessary actions to correct them. Such investigations are possible due to the Trade Act of 1974, sections 301 to 310.
Any country trading with the US can be subject to a 301 investigation. In fact, the USTR actually releases an annual report of various countries and whether they’re on a trade watch list. Why is this important? Read on; it’s about to get good.
I’m going to review the specific actions as well as all the tariffs resulting from the 2017 USTR investigation caused by the suspicious trade behaviors of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) regarding US imports. After the investigation, China was found to be guilty of four different trade practices negatively affecting our domestic economy.
First, they forcibly acquired intellectual property (IP) and vital technologies from US companies by requiring them to disclose important details with prying approval processes or joint venture requirements. This was a direct violation of IP rights protections.

They also enforced their restrictive policies, disabling the US to set market terms for price negotiations and licensing.
Furthermore, China’s government invested in domestic companies across targeted industries that would substantially hurt the assets of US companies and their standing in PRC’s economy.
And they supported unauthorized access to secure data networks, making it possible for data miners to steal trade secrets and vital information from US businesses.
As a result of these findings, the U.S. government imposed a series of tariffs on Chinese goods to make up for the money they were losing due to those policies and illegal technology transfers. These were initially implemented in 2018 and specified by a commodity’s Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) classification code.
Further reviews have resulted in a total of four different HTS code lists with varying tariff rates. By the end of it, thousands of imports from China had tariffs applied, from nuclear reactors to baby onesies. Even so, I’m going to break down the process of how it happened list by list, since that affects certain rates and exclusions.
Warning, Will Robinson, warning…the details below are quite extensive. Before diving deeper, let me take this opportunity to remind you that it may be best to have a consultation with a customs brokerage expert. Call (855) 912-0406 or submit a request online for all of your Section 301 tariff needs.
The first list of products affected by new tariffs was directly related to the initial accusations against China in regard to the acquisition of US technologies. The majority of items on this list are industrially significant technologies.
Overall, the products covered represent about $34 billion worth of imports. There were a total of 1,333 commodities defined by their eight-digit HTS subheading code included and were being charged an additional 25% tariff on top of the normal trade relation (NTR) rates. Products on this list came from the following HTS chapters:
This didn’t include every HTS subheading under the chapter, meaning it was still possible to import certain types of items in these categories. As the trade war went on, those exceptions went away.
In August 2018, only a month after the first list went into effect, a second list made up of another $16 billion worth of imports was introduced. It included 563 additional HTS subheadings. Like List 1, this one was also originally subject to a 25% tax.
List 2 continued the theme of taxing industrial materials, but applied to some of the raw materials that got left out of the first list. Additional items under the following chapters were affected:
The tariff rate add-ons may have ended here, limited to the most critical industries focused on by the USTR investigation. Of course, that’s not what happened, and we got List 3 and 4 instead.
List 3 is where things began to get messy. As a result of the first two lists, China issued a retaliatory 25% tariff on US goods, valued at $50 billion—equivalent to the US tariffs on China.
The third list was then drafted and put into effect just a month after List 2 in response to China’s retaliation. When the tariff was first put into place in September 2018, it added a 10% duty on top of NTR rates. By May 2019, it increased to a 25% tariff.
New These drastic increases were meant to deter China from issuing another retaliatory tariff in response. List 3 expanded on the 15 chapters worth of commodity codes already covered by the first two lists, and then added subheadings from 66 other HTS chapters.
By this point, 81 chapters worth of HTS classification had some kind of additional tariff requirement; that’s just under 8,000 commodities. Their total value? Over $200 billion.
Unlike the first two lists, the items in List 3 have little relevance to each other. It’s vast and encompassing, and really just aimed at gathering enough items together to reach the needed value to deter further retaliation from the PRC.
After a year’s worth of continued tension between the two nations in regard to trade, a final list was drafted to include the rest of the goods not already covered by one of the first three lists.
It finished expanding the list of subheadings of previously specified chapters and included every classification from the 14 chapters that had yet to be affected.
The import value of items making up list 4 amounts to approximately $300 billion. The good news for importers was that around the same time, the US and China began drafting a new trade agreement.
The adoption of the Phase One trade agreement in January 2020 resulted in this final list being divided into an ‘A’ and ‘B’ list. Thanks to the agreement, tariffs were only added to one of them.
- List 4A: A 10% tariff on 3,243 HTS subheadings went into effect September 2019. The rate was later lowered in February 2020 to 7.5% per the details of the Phase One agreement.
The subheadings free from the heightened tariff rates stretch across 51 different chapters of the HTS, but in varying quantities.
For instance, chapters 60 to 63 are largely made up of clothing items, and multiple classifications are on the 4B list. The great variety of products covered provides importers with a wide range of possible imports.
However, chapter 28, which includes codes for various inorganic chemicals, has only one commodity free from tariff—sodium bromate—a compound whose most exciting tasks involve batch dyeing and is easy to produce. Not exactly a great profit generator.
If you’re importing items that may fall under any of those 51 chapters where list four wasn’t fully implemented, be sure to work with an experienced customs broker. Correct classification can be the difference in thousands of dollars worth of import duties.

The products that made up the 4B list are the only ones that don’t carry an additional tariff duty when imported from China. As mentioned, these include products from 51 different chapters of the U.S. Harmonized Tariff Schedule, but not necessarily every commodity within those chapters.
There are items on other lists that may receive lower duties thanks to specifically granted exclusions, but those are not permanent and can be specific only to the organization that requested the exclusion.
Anyone who's really been counting chapters at this point might realize we’ve covered 96 of the 99 chapters that make up the entirety of the U.S. HTS, so there’s hope that some chapters are free and clear, right? Not really, and here’s why.
There are two other options for importing products from China that don’t carry the additional tariff. Let’s cover the fine print involved in importing from both Taiwan and Hong Kong.
The government of the People’s Republic of China has claimed Taiwan and considers it one of its (renegade) provinces. Despite this claim, Taiwan is an independently governed island, recognized as such by the international community.
You might get confused about its status because Taiwan is officially recognized by two other names
You can see where the muddling of whether Taiwan is China comes into play. Even so, it remains self-governed, so the additional tariffs imposed by the US on the PRC do not apply to Taiwan.
Importers could technically benefit from a wide range of products made here, and there are clear signs of that happening. Import origin reports from the Observatory of Economic Complexity continue to track a steady increase in products entering the US through Taiwan.
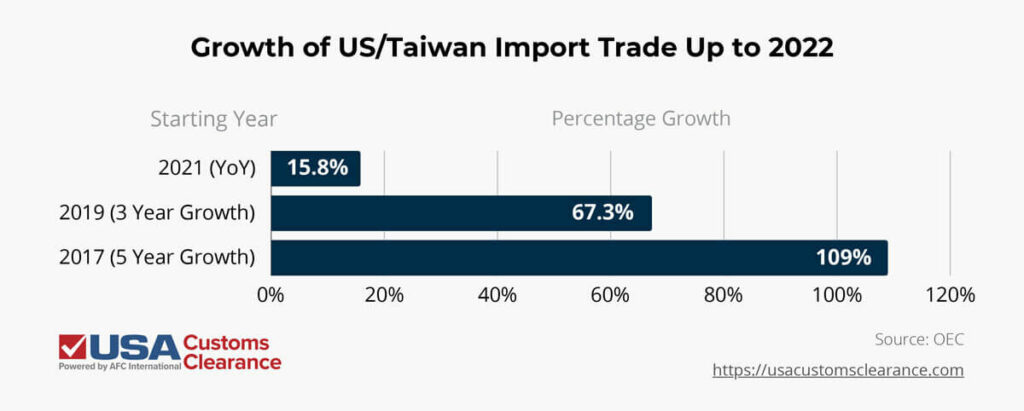
As good as the manufacturing growth is, in reality the nation cannot fully replace the range of products affected by the current tariff hikes. Although business in Taiwan has grown, it simply does not have the same output capacity as mainland China.
Hong Kong has legally been overseen by the PRC as a special administrative region since 1997. The island, and nearby Macau island, enjoy a great deal of autonomy when it comes to business and trade.
For many years, products made here were exported and sold as “Made in Hong Kong”, making it visually distinct from China. However, on July 14, 2020, Executive Order 13936 was signed which changed the country of origin requirement for labels. Now, any goods manufactured in Hong Kong are marked as “Made in China”.
Despite this, in terms of official trade, the US continues to treat Hong Kong and the PRC as separate entities. Hong Kong retains a unique ISO country code that can be applied for international trade purposes.
Products with a Hong Kong ISO code are not subject to additional duties under Section 301.
If you've imported products from Hong Kong and have been incorrectly charged section 301 duties, contact us. We'll work with you to file a Post Summary Correction (PSC) in order to fix this mistake and receive all refunds for which you're eligible.

Tariff hikes like the ones imposed on Chinese products can place a significant monetary burden on importers because they’re intended to make the products cost the same or more than similar domestic products.
Some tariffs being levied against China have been set high enough to effectively act as a product ban. Between the tariff rate, NTR, and shipping costs, your chances of making any kind of profit are nonexistent.
However, if the tariff hike is only intended to bring up the cost to somewhat match domestic competition, there’s hope. Either the importer takes a significant cut off their profit margin, or ends up increasing the sale cost of the product to cover the new overhead.
Of course, you have the option to avoid the tariff all together, but that can be easier said than done. Next, I’ll go over various legal ways to get around the tariffs or to limit their impact on your business.
Importers can reduce the immediate impact of the tariffs by utilizing a Foreign Trade Zone (FTZ) or bonded warehouse. These are places within US borders that can be used to store imports without paying the tariff duty.
Duty is only paid when the items are removed from the FTZ and enter the domestic market. This kind of strategy can be tremendously beneficial, especially to small businesses.
This solution has some downsides though. For instance, the costs of using such spaces. Also, you’re not actually avoiding the tariff so much as lessening the full impact of it by being able to pay it in increments as you move items into the domestic market.
If you’re importing for re-export, then yes, the entire 301 tariff is avoided.
Section 301 provisions leave room for tariff exclusions which can remove or reduce the duty rate you’ll need to pay for specific products. In order for the product exclusion request to be considered, the following information should be sent to the USTR:
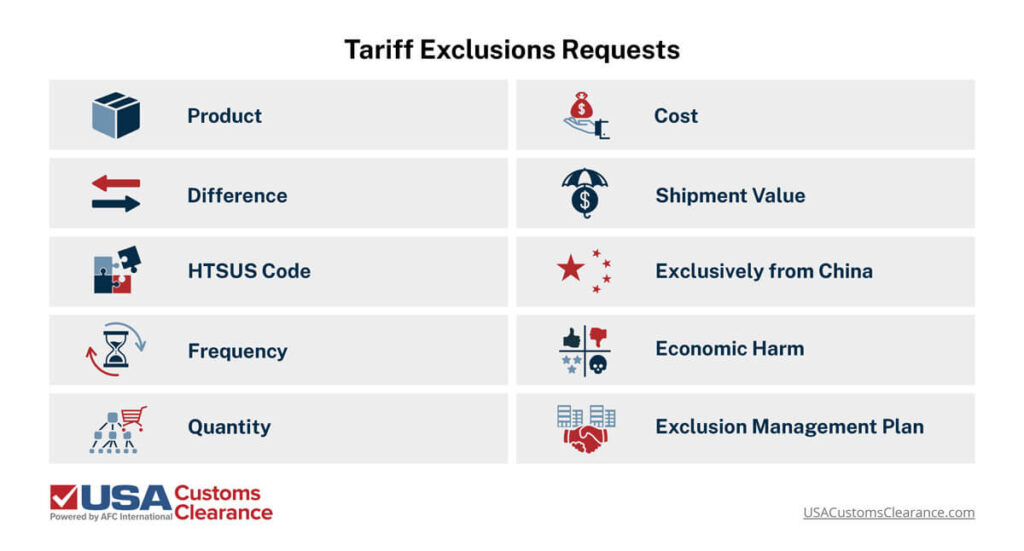
List The tariff exemption can apply to just the one importer with a specific product, or the USTR can choose to add it to a list of products that any importer would be able to benefit from.
If an exclusion is granted, the product will be completely free from the 301 duties. On the downside, it’s only good for a year after the decision is published, and then the duties will be added again.
If an exclusion is granted after you already imported and paid duties, you have the option to request a refund. Learn more about how to do this on our blog, Tariff Refund: Eligibility and How to Apply.
From the time the tariff increases started taking effect in 2018 and throughout the add-ons and modifications, the USTR has continued to accept applications for exclusion requests. Up until exclusion requests were made private, the Congressional Research Service (CRS) recorded over 53,000 applications. On average, just 13% of these were granted.
The exclusions included a limited number of products from all four lists, most of which are now expired. Anyone wishing to be granted an exception will have to apply specifically to the USTR should they allow an extension.
For a list of specific product exclusions, it’s best to work with a professional customs broker familiar with the specific HTS codes involved.
Another option for some importers is a duty drawback, when imported goods are later exported or properly disposed of within three years.
There are four versions of duty drawback that imports are more likely to qualify for with Section 301 commodities.

The most important documents involved in the process of applying for a drawback are the specific one being applied for, proof of exportation, and US manufacturing records. Learn even more about Section 301 Duty Drawback here.
If you feel that your product falls under an exclusion or is one of the 4B list items that never received a tariff increase, and you’re still being charged, your product may have the wrong HTS code.
In the case of potentially misclassified products, you can submit a request to the CBP or to a qualified customs broker for product reclassification.
To submit a classification request, you will need to submit specific information to CBP about the product in question:
Going through reclassification can be a bit of a hassle, but if you’re right, that could be up to several thousand dollars in duty fees saved.
Section 321 De Minimis, also called Section 321 ACE, are provisions that allow certain products to be imported duty-free.
For instance, chapters 60 to 63 are largely made up of clothing items, and multiple classifications are It might sound too good to be true, but that’s because you need to meet very specific criteria to qualify.
When filing an informal 321 De Minimis shipment, no customs bond is required and no duties need to be paid. However, customs will only release one such shipment to one entity per day, which is not a practical solution for most large-scale companies.
Smaller companies that work with less inventory at a time can certainly use this provision for their benefit. Provided you meet the list of qualifications, it’s probably the best way to avoid extra tariffs outright.
Think this is for you? Read on about Section 321 Shipments.
If none of the other solutions presented work for you, and the additional tariffs are simply too much, then the only reasonable option left may be to find another supplier.
In the case of products or raw materials, finding other suppliers is a little easier. There are a number of online B2B marketplaces where you can search for products. You may have started with Alibaba, but there are dozens of alternates available. Discover the Top Alibaba Alternatives.
Because of the ongoing trade tensions between the US and China, several countries have been improving their own manufacturing industries to offer quality, competitive products.
Countries in Asia worth taking a closer look at as potential suppliers include:
For businesses considering moving the actual manufacturing centers and offshoring facilities, there’s a bit more headache involved. Shifting manufacturing is a massive undertaking, especially for larger companies.
Some of the more popular destination options for these moves are the countries we’ve just mentioned. However, Mexico has also emerged as a contender in the race to relocate US-owned manufacturing centers.
The chance to access a ready labor pool and reduce shipping costs has many businesses focused on nearshoring their operations to the United States’ southern neighbor or other countries in Central America working on growing their manufacturing capabilities.
Section 301 tariffs have disrupted the normal operations of thousands of companies, and many are scrambling to find ways to overcome the chaos. To make sure yours doesn’t fall by the wayside, you’ll need a strong strategy for overcoming the increased costs.
There is no perfect solution, but the experts at USA Customs Clearance can help you find options that best suit your business’ needs.
Get ready to solve your Section 301 issues. Call (855) 912-0406 or submit a specific request online.
For Chinese import tariff updates in 2024, please see "US Tariffs on China Imports Are Not Going Away".
You can also stay updated on this year's tariff tiff here, "Made in China 2025 vs. US Tariff Strategy: Who’s Winning?"
 Copy URL to Clipboard
Copy URL to Clipboard
what does moldova bring to the us bruh
Hi Divij,
Interestingly, the US imported over $142 Million goods from Moldova as of last year. The list is way too long to put here though, my friend. Please feel free to check out the United Nations COMTRADE database on international trade for those specifics.
But since I don't want to leave you hanging completely, I'll give you the top 3 imports from Moldova in 2024:
1. Beverages, spirits, and vinegar
2. Vegetable, fruit, nut food preparations
3. Articles of apparel, not knit or crocheted
Thank you for informative article and current updates
You're most welcome, Raya. We greatly appreciate your feedback.
Have a fabulous day!
DO Samples still qualify for section 301 tariffs .. example 9817.85.01
Hi Tiffany,
If you’d like an expert to walk through the specifics of your HTS code (and confirm it's the correct one), current tariff rate, and any open exclusions, we can connect you to one.
You can start that conversation online here. https://USACustomsClearance.com/contact
A Licensed Customs Broker can make sure you have the most accurate information before you commit to any import.
Hope this helps point you in the right direction—and keeps you ahead of the ever-moving Section 301 goalposts!
If a product (like a plastic bottle) is being sent to China for decorative logo painting or hydrograph printing, and being shipped back to the U.S. company, would the service charge by the Chinese company be subject to tariffs?
Hi Frank,
Good question, but not a typical or standard import scenario. That said, your Licensed Customs Broker can help identify what costs you can expect, and determine how much you’ll owe in duties and tariffs for your unique customs and import needs.
Here's where to get started to have that important conversation.
https://USACustomsClearance.com/contact
If I import the Manufactured Homes, TYPE Mobile Homefrom CHINA,This type the product have any DUTY? if yes How much? or is EXEMPT?
Hi Carlo,
Great question, though please note that I can’t give you a definitive duty rate or tell you exactly how Section 301 will apply to your shipment. Simply put, there's more info needed.
As an importer, there are some things you need to work through before the goods hit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). Like:
> Pinning down the correct 10-digit HTSUS code for each product
> Verifying whether the code appears on any of the Section 301 lists (1 through 4A) or on the new lines added in the USTR's four-year review
> Checking active exclusions
> Ensuring you're using the correct date since there's a nuance to it
> Exploring mitigation tools such as duty drawback, etc. after you know the precise duty profile
Partnering with a Licensed Customs Broker is so valuable to help make sure you're dotting all the i's and crossing all the t's. Plus, they can help model savings too.
Here's where you can get this started, Carlo.
https://USACustomsClearance.com/import-consulting-services
We're excited to hear back from you on how your manufactured home importing goes!
any update on 321 being rescinded?
Hi Jin,
You can find all updates on Section 321 tariffs here.
https://USACustomsClearance.com/process/section-321-shipments
And if you'd like to keep an eye on all tariff news easily, check out our Import Tariff News page that's updated up to 10x every week.
https://USACustomsClearance.com/import-tariffs-updates/
If a product is imported from another country than China but contains many Chinese components, how is it determined if the product should carry any Chinese tariffs?
Hi Arne,
Good question and not a typical scenario.
Your total costs vary depending on the value of your imports and what kind of products you plan on importing.
That said, your Licensed Customs Broker can help identify what costs you can expect, and determine how much you’ll owe in duties and tariffs for your unique customs and import needs.
Here's where to get started to have that important conversation.
https://USACustomsClearance.com/import-consulting-services
Hi
Can you tell me what import rules I need to know to import resin and hardener kits for artists?
Is there a chemical registration body I need to apply to?
Also do you assist non US residents with importing?
Thanks
Hi Miranda,
Great questions. Because importing rules are so specific and it's important to ensure the correct HTS codes are being used, it's best to get direct professional, expert customs brokerage support. For your convenience, here's the link to start that conversation. https://USACustomsClearance.com/contact
And we're checking on your non-US resident question as well. However, you may get a faster response on that via the contact form link as well.